Basic Differences Between Print and Digital
It is important to differentiate between graphics for print and graphics for digital items. Computer monitors emit light to display colors, whereas inked paper absorbs or reflects different wavelengths of light to produce color. Each type has the ability to display a different gamut—a limited range of the visible spectrum of light. These ranges do not entirely overlap, so items on the screen will often look very different when printed.
The other important difference is that of resolution. Items on the web have lower dpi (dots per inch) while print pieces have much higher dpi in order to preserve the utmost quality when printing. Images on the web are sized according to the number of pixels.
RGB vs. CMYK
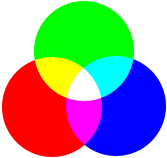
Digital: RGB
RGB stands for red, green, and blue—the colored light that monitors display. This color model is additive, meaning these colors are added together in various ways to create a wide range of colors. A combination of two colors at full strength can create the secondary colors cyan, magenta, or yellow. A combination of all three at full strength creates white.
Print: CMYK
CYMK refers to the four inks used in most color printing: cyan, magenta, yellow, and key (black). This color model works by masking colors on a lighter surface (such as white paper) and reducing the light that would be reflected to the human eye. This is called subtractive color because the ink “subtracts” brightness from the white paper.
Two colors combined at full strength can create the secondary colors red, blue or green.
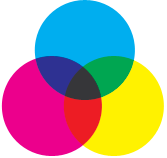
Why is K “Key”?
The K stands for “key” because the colors in four color CMYK printing are “keyed” or aligned, with the “key plate.” The key plate provides lines, contrast, or other details in printing and is usually black.
Vector vs. Raster
Vector Art
A vector image is created with mathematical points, lines, and curves, and can be scaled infinitely, both larger and smaller, with no loss of quality. Vector files cannot be easily used on the Web; however they can be used to make files to be placed on the Web with image editing software. Vector file formats are commonly created using Postscript programs such as Adobe Illustrator and Adobe InDesign, and usually have a .eps or .ai extension. Vector files are the best format to use when printing any version of the CSU logo.

When zoomed in, the image still looks crisp.
Raster (AKA Bitmap) Art
A raster image, also known as a bitmap image, is comprised of a series of small squares called pixels. Each pixel contains unique information about its color. If a raster file needs to be enlarged, the computer has to guess (or interpolate) to create new pixels between the old ones. This can result in the image becoming blurry when the size is increased. Raster file formats include .jpg, .tif, .gif, .png, and .psd extensions.
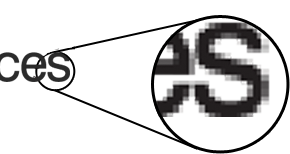
When zoomed in, the image looks pixelated.


