Getting Started with Web Content
The Priority Tasks below are based on the emerging and developing steps of the Electronic Accessibility Rubric. Completing the Priority Tasks will help you meet the universal design goal for web content. Using the rubric helps to prioritize the easiest steps and those that will have the most impact.
The Advanced Tasks are necessary to make a website fully accessible, but we advise mastering the priority tasks first.
If your content has complex images and multimedia, make sure to check their additional entries in the rubric.
Priority Tasks
Headings
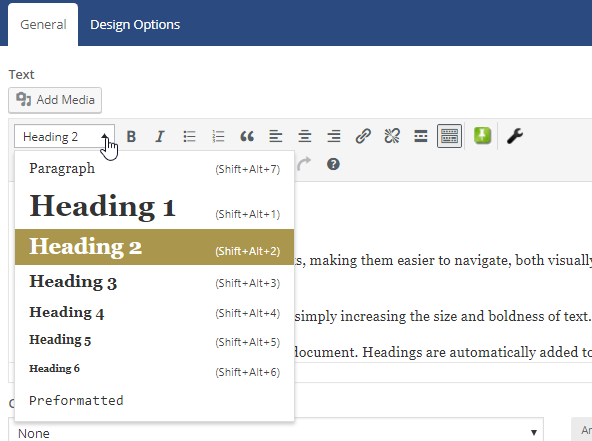
In the text editor, use the Paragraph drop-down menu to select heading levels.
Descriptive Links
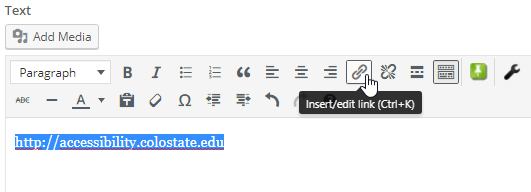
Select the link text, then click on the Insert/Edit Link icon.
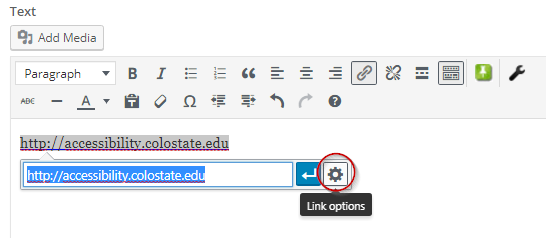
Click on the Settings button to get more Link Options.
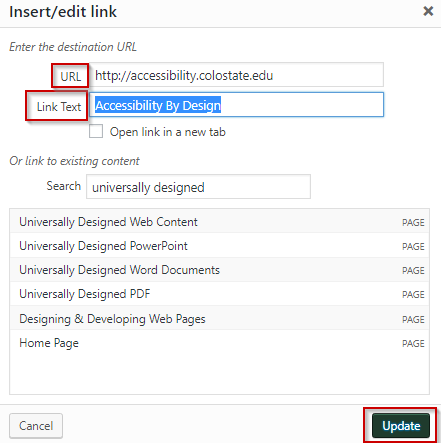
In the Link options window, enter the destination URL and the descriptive link text in the appropriate fields. Once these are both added, click Update to apply changes.
Alternative Text
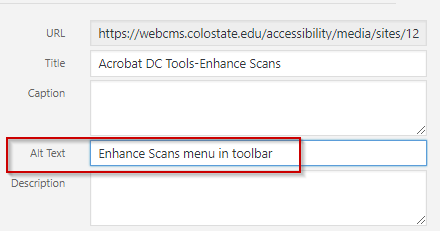
Using the Media Library
To add alternate text in WordPress, click on the image in the Media Library and edit the Alt Text field.
Coding in HTML
When editing HTML code directly, include the alt attribute (“alternative text”) for all images. The alt attribute is added after the path to the file:
- Example: <img src=”file-name.jpg” alt=”Descriptive text goes here.” />
Alt text should describe the meaning of an image rather than its appearance. For example:
- Poor: <img src=” lab_sign.gif” alt=”Sign hanging on lab door.” />
- Better: <img src=”lab_sign.gif” alt=”Each laboratory has safety policies posted on the door.” />
Purely decorative images (graphics that convey no information), require a “null” or “empty” alt attribute. The null attribute is a signal to screen reader software that the image is unimportant and can be skipped. Use this with caution – ensure that the image truly is only decorative.
Example: <img src=”spacer.gif” alt=”” />
Table Header Row
- Use tables for tabular data only, not as a framework for page layout.
- Keep tables as simple as possible, and try to avoid nesting tables inside one another.
- Add captions to tables using the <caption> tag. A caption will typically provide an adequate summary of the table’s contents. Complex tables may need a more detailed explanation using the <table> tag’s “summary” attribute.
- Use a plugin that marks header rows correctly as <th>. If this is not possible and you have to edit the code manually, replace <td> (table data) tags with <th>(table header) tags to indicate the special function of those cells as column labels.
Advanced Tasks
Color Contrast
Ideally, your template should have been designed with colors that have good contrast. Visit Color Contrast Tools page for methods of checking the colors on your site.
Video Player and Captions
- Use a video player that can be controlled using a mouse, a keyboard and a screen reader
- Use a video player with visible controls to toggle captions
- Provide accurate captions for videos and accurate transcripts for audio files
- Provide audio description for videos
For available captioning solutions, visit Video Captions page.
Accessibility Checker
- Visit Web and Software Application Tools for more information on accessibility checkers for websites.


