What are Transcripts?
Transcripts provide an accurate text version of audio content, either for video or audio files. They’re usually a downloadable document, most commonly in Word format.
Video Transcripts
Transcripts are different from captions in that the text is not displayed in sync with the video. Since a transcript is viewed separately from the video file, it needs to include logical formatting (including headings) and to make sense on its own.
To provide an equitable experience of videos, synchronized captions are required; transcripts are not usually sufficient. However, there are cases where transcripts may be preferred or required, especially in an academic setting, so having both available is recommended.
Audio Transcripts
For audio-only files, a transcript is the only method of providing a text alternative. This can either be a downloadable document or text can be displayed alongside the audio file.
When audio files are embedded in another document, such as a PowerPoint file, a separate transcript is still needed.
Interactive Transcripts
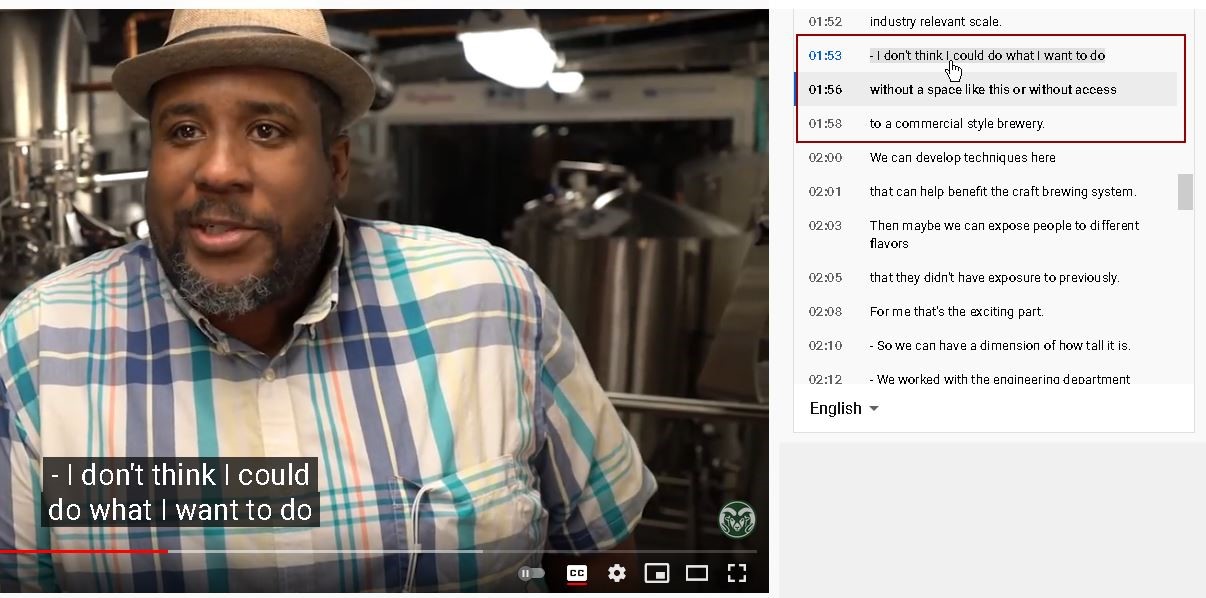
Another type of transcript is now available through some video players. Platforms such as YouTube or Kaltura can turn captions into an interactive transcript, with text that displays alongside the video. The text is synchronized with the audio, and scrolls as the video plays.
Interactive transcripts are both searchable and clickable, meaning that you can find a specific point in a video and jump to it. In the screenshot, you can see an example of an interactive transcript displayed next to a video.
Why Use Transcripts?
Transcripts support many different learning strategies, such as
- Learning new vocabulary
- Learning new language
- Note-taking
- Focusing
- Reviewing
- Searching for terms
- Going directly to a specific point in a video
The following video demonstrates the benefits of interactive transcripts in particular.


